Updated September 22, 2023
A Wisconsin parenting plan is a document assigning the childcare responsibilities of each parent in light of a legal separation, divorce, or paternity case. The agreement covers legal decision-making authority, financial obligations, physical custody, visitation rights, and more. Legal custody and physical placement are treated as distinct issues under Wisconsin law.
Child Custody Factors
When a custody case is brought before a court, the court will evaluate a wide variety of factors in order to determine what serves the best interests of the child. These include:
- The wishes of the child and the parents
- The willingness of the parents to cooperate and communicate with one another
- The willingness of the parents to support the child’s healthy relationships with other family members
- The child’s history with each parent, including quality time spent together
- Lifestyle adjustments for the child, including education, religious observance, and community
- The child’s age and developmental needs
- Any criminal records or history of drug abuse on the part of a parent, a parent’s spouse, or anyone who resides with the parent
- Any history of battery or domestic abuse
- Expert testimony if admitted into evidence
- Any other factors deemed relevant by the court
Table of Contents |
How to File for Custody in Wisconsin
The process of filing for custody can take place as part of a divorce, legal separation, or paternity case.
If the parents are unmarried, paternity will need to be established before the custody process begins. This can be achieved with a paternity test or by filing a Voluntary Paternity Acknowledgment form. Once paternity is conclusively determined, the custody laws and proceedings apply equally to married and unmarried parents.
In cases involving domestic violence, parties can seek immediate legal protection via a temporary restraining order.
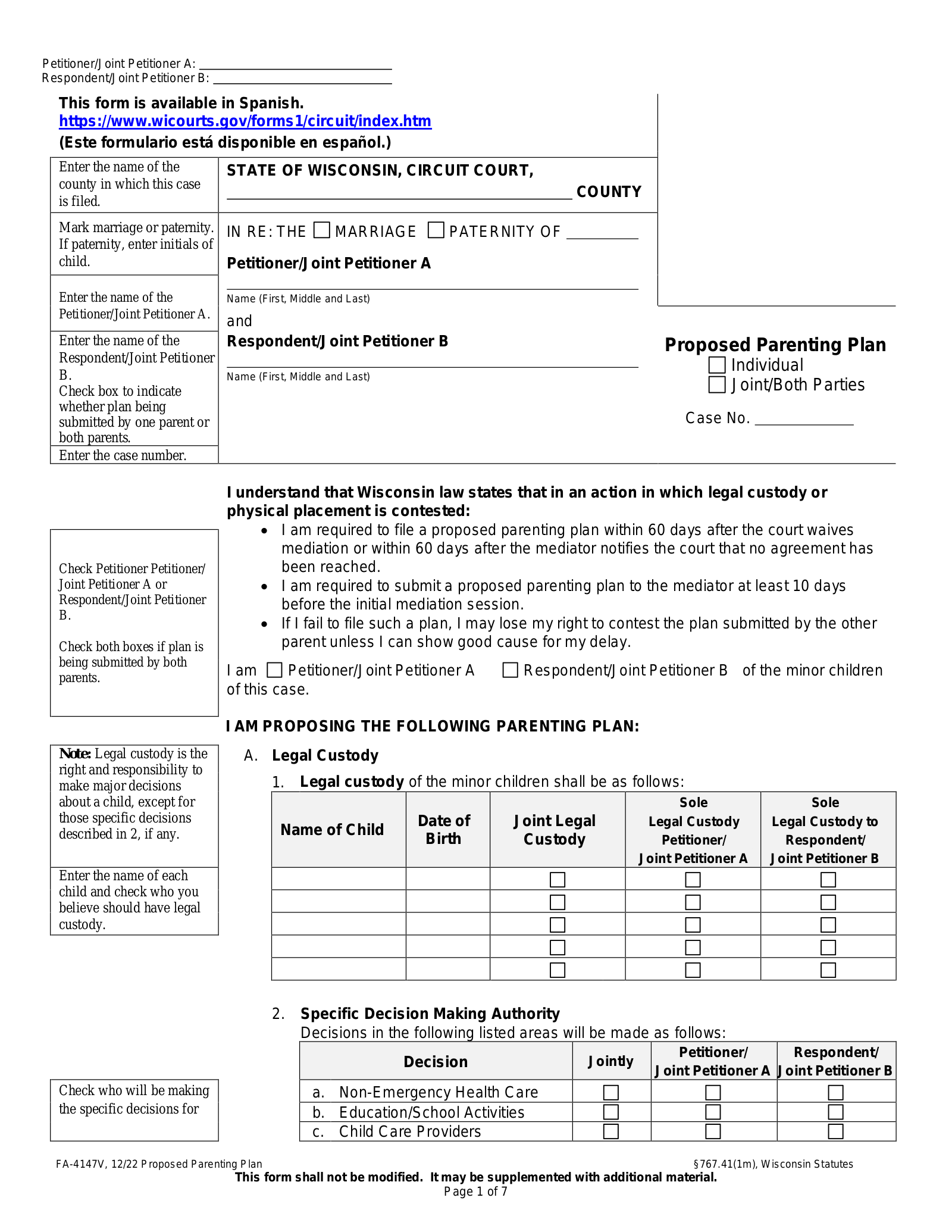
1. Agree on a Parenting Plan
Parents are encouraged to work together on a proposed parenting plan that suits their unique needs. If both parents agree to all the terms of custody—such as scheduling, visitation, parental responsibilities, and other relevant arrangements—the court is likely to approve it as long as it is determined to serve the child’s best interest.
Under state law, parents must submit a proposed parenting plan to the mediator at least 10 days before the first session. If a party fails to submit a proposed plan, they may forfeit their right to contest the other party’s proposal.
2. Calculate Child Support
Use the state’s worksheet and calculator to estimate how much the court may order in child support obligations.
3. File Required Forms
Once completed, file the proposed parenting plan along with other required documents for approval with the family court commissioner in the circuit court of the county where the child resides.
4. Attend Mediation
The court will refer the parties to mediation when an agreement cannot be reached independently.
5. Trial and Judgment
As a last resort, the court will step in to render a judgment regarding legal custody and physical placement. Once the court receives notice from the mediator that no agreement was reached (or upon the court’s decision to waive mediation), the proposed parenting plan must be filed within 60 days (§761.41(1m)).
The court will appoint an attorney to represent the best interest of the child in the proceedings. A legally binding custody order will be put into effect based on the outcome of the trial.
Custody Laws
- Child’s Preference: § 761.41(5)
- Visitation (Third Parties): § 48.925
- Visitation (Grandparents and Stepparents): § 48.9795(12)
- Court Ordered Parenting Classes: § 761.401
- Uniform Child Custody Jurisdiction and Enforcement Act: Wis. Stat. Chapter 822
Related Forms