Updated April 12, 2024
A Wisconsin deed is a document that helps to transfer and convey property from a grantor (the seller) to a grantee (the buyer). The form is a simple 2-page document that describes the two (2) parties along with the property and the purchase price (known as ‘consideration’). The form must then signed, by the Grantor(s) only, in front of a Notary Public. The deed may then be brought to the County Register of Deeds along with the filing fee and the Real Estate Transfer Return.
Laws – Chapter 706. Conveyances of Real Property; Recording; Titles
Real Estate Transfer Return (eRETR) – This form must be filed along with any deed recorded in the State of Wisconsin (See Instructions).
Recording – Must be filed with the County Register of Deeds in the jurisdiction of the property being conveyed.[1]
Signing – All signatures by the Grantor(s) must be accompanied by the acknowledgment of a notary public.[2]
Deed Types (4)
 General Warranty – Provides guaranteed ownership of the property to the buyer (grantee) with no defects on the title.
General Warranty – Provides guaranteed ownership of the property to the buyer (grantee) with no defects on the title.
Download: PDF, MS Word, Open Document
 Quit Claim – Only transfers the implied ownership interest the seller may have in the property. Does not guarantee title to the buyer.
Quit Claim – Only transfers the implied ownership interest the seller may have in the property. Does not guarantee title to the buyer.
Download: PDF, MS Word, Open Document
 Special Warranty – Guarantees that the title does not have any blemishes or defects during the course of the seller’s ownership period.
Special Warranty – Guarantees that the title does not have any blemishes or defects during the course of the seller’s ownership period.
Download: PDF, MS Word, Open Document
 Transfer on Death – Allows a person to transfer their interest in a property to a beneficiary and enables the beneficiary to skip probate.
Transfer on Death – Allows a person to transfer their interest in a property to a beneficiary and enables the beneficiary to skip probate.
Download: PDF
Wisconsin Property Search (3 steps)
When completing a deed, the Legal Description needs to be written on the form. Therefore, you will need to pull the deed information from the County it is located. The numbers you want to obtain are the Tax Map/Lot Numbers, Parcel ID (if any), and the Deed Book and Page Numbers.
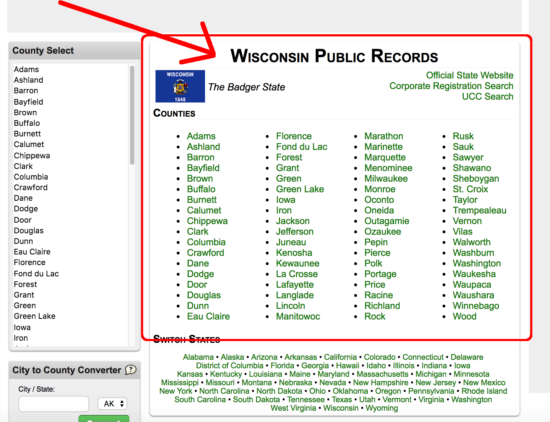
Step 1
Go to this public records database and select your county.
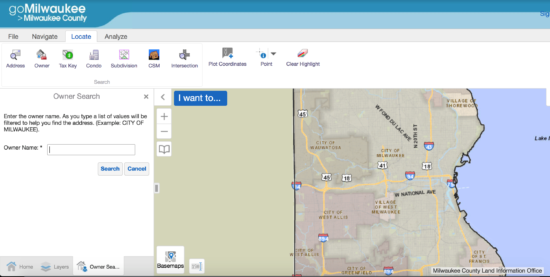
Step 2
For this example we will use Milwaukee County (click to launch the viewer on the map). When you go to your County or City Assessor you will want to perform a lookup by the Grantor’s name. That will ensure they in fact own the property and be able to find the Legal Description.
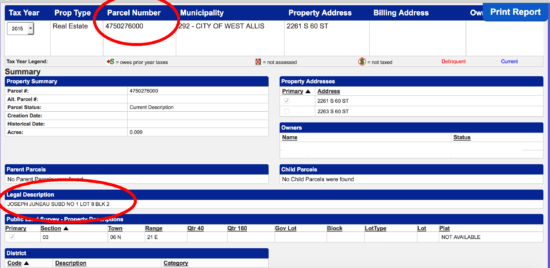
Step 3
When you have found the property you can find the required information including the Parcel Number and the Legal Description. This can be written in the deed to satisfy the Recorder.