Updated March 20, 2024
A 1099-SA form is an IRS tax document that reports distributions made from a health savings account (HSA), Archer medical savings account (Archer MSA), or Medicare Advantage MSA (MA MSA). The trustee or custodian of the savings account is responsible for filing Form 1099-SA with the IRS and furnishing a copy to the account beneficiary.
Important to Know
If you receive a 1099-SA, you will need to report the distributions from your savings account when you file your taxes, even if the distributions aren’t taxable income.
Table of Contents |
Who Gets a 1099-SA?
A 1099-SA is typically issued to the holder or beneficiary of an HSA, Archer MSA, or MA MSA to report distributions made from the account.
Death of the Account Holder
If the account holder dies, the savings account is inherited by a designated beneficiary. If the designated beneficiary is not the surviving spouse, then the account ceases to be an HSA/MSA. In this case, the remaining assets are paid out to the named beneficiary, who will then receive Form 1099-SA.[1]
Using Form 1099-SA
Distributions from an HSA/MSA are not considered taxable income as long as they were used for qualified medical expenses.[2] However, you are still required to report these distributions when you file your taxes, using either Form 8853 (Archer MSA) or Form 8889 (HSA).
Deadlines
The deadline to file Form 1099-SA with the IRS is February 28 of the following year, or March 31 if filing electronically. If the deadline falls on a weekend or federal holiday, the deadline to file is extended to the next business day. However, the filer must furnish Copy B to the account holder or beneficiary on or before January 31.[3]
2024 Deadlines
- January 31, 2024 (recipient)
- February 28, 2024 (IRS–Filing by Paper)
- March 31, 2024 (IRS–Filing Electronically)
Form Parts (12)
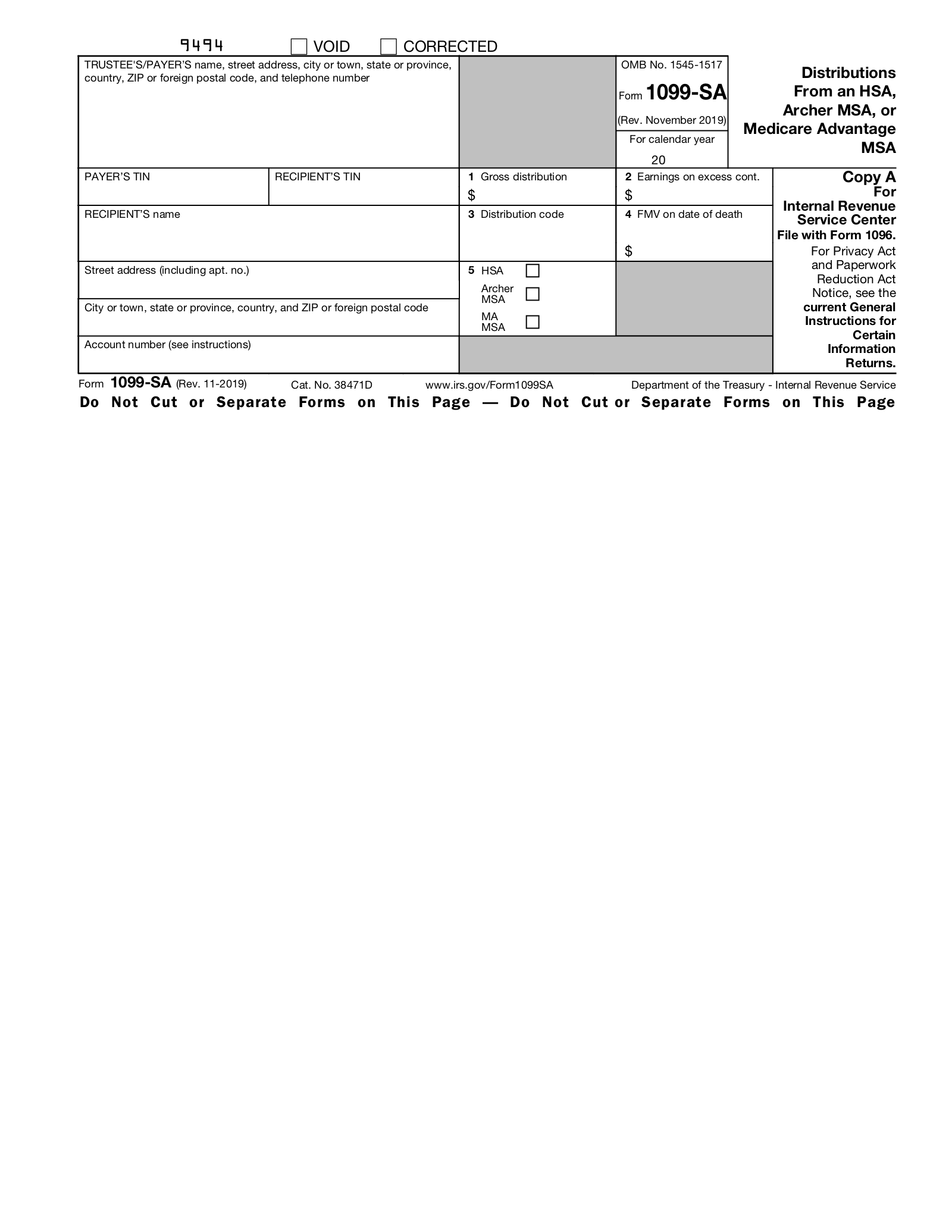
1. Gross Distribution
Enter the total amount of the distributions from the savings account during the calendar year. Include any earnings on excess contributions, which are also reported in Box 2.
2. Earnings on Excess Contributions
Enter the total amount of distributions resulting from the return of excess HSA or Archer MSA contributions. If no earnings on excess contributions were distributed, put a 0 in this box.
3. Distribution Code
In this box, enter one of the following distribution codes, depending on the circumstances:[4]
- 1: Normal distributions where no other code applies.
- 2: Distributions of excess HSA or Archer MSA contributions.
- 3: Distributions made after the account holder became disabled.
- 4: Payments to a decedent’s estate in the year of or after the account holder’s death. (i.e., death distribution other than code 6)
- 5: Distributions used for purposes other than qualified medical expenses. (i.e., prohibited transactions)
- 6: Payments to a decedent’s non-spouse beneficiary, other than an estate, after the year of death.
If you receive Form 1099-SA with code 5, you may owe additional money to the IRS in taxes and/or penalties.[5]
4. FMV on Date of Death
Enter the fair market value of the account as of the date of the account holder’s death. If you are not filing Form 1099-SA as the result of the death of an account holder, leave this box blank.[1]
5. Checkbox
In this box, check the corresponding box to indicate if the distributions were made from an HSA, Archer MSA, or MA MSA.
6. Identifying Information (6 Entries)
On the left side of the 1099-SA, a total of 6 boxes require information that identifies the payer and recipient, including:
- Trustee/Payer information – name, full address, and phone number
- Payer’s TIN – taxpayer identification number
- Recipient’s TIN – normally an SSN/ITIN or EIN
- Recipient’s name – full name
- Recipient’s street address – number and street only
- Recipient’s remaining address – city/town, state/province, country, Zip/postal code
The recipient’s TIN must be entered in XXX-XX-XXXX (SSN or ITIN) or XX-XXXXXXX (EIN) format on Copy A of this form.[6]
7. Account Number
The account number field is generally provided for the payer’s reference and for internal recordkeeping. It is required if there are multiple accounts for a recipient who is receiving more than one 1099.
The IRS encourages you to designate an account number for all 1099-SA forms that you file. Note that the account number must be unique and cannot appear anywhere else on Form 1099-SA.[7]
Instructions (5 Steps)
1. Collect W9
In order to have the correct information to file the 1099-SA, the payer must first collect a W9 form from the recipient. The W9 provides information needed to fill out the form, such as:
- Name
- Mailing address
- SSN/ITIN or EIN
2. Obtain the Form
Form 1099-SA is available as an online fillable PDF. If you are filing by paper, you may file a black-and-white Copy A that you print from the IRS website, along with IRS Transmittal Form 1096.[8]
3. Copy A – IRS
If filing by paper, Copy A, along with Form 1096, must be filed with the IRS by February 28. The mailing address to which you send these paper forms will depend on the home state of the filer. If filing electronically, submit Copy A to the IRS by March 31.
4. Copy B – Recipient
Copy B must be furnished to the recipient by January 31 of each year. Use the address listed on the W9 form to send Copy B to the recipient.
5. Copy C – Keep
Keep Copy C in your records for at least four years. The IRS may request the form in the event of an audit or investigation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is considered a qualified medical expense?
Generally, “qualified medical expenses” for HSA purposes are unreimbursed medical expenses that could otherwise be deducted according to Schedule A (Form 1040). Qualified medical expenses can be paid on the behalf of the account beneficiary, their spouse, and/or their dependents.[9]
What is the difference between Form 1099-SA and Form 5498-SA?
Form 1099-SA is used to report distributions made from an HSA, an Archer MSA, or an MA MSA. Form 5498-SA must be filed by the trustee or custodian of an HSA/MSA for each person on whose behalf an account was maintained, regardless of whether any distributions were made.[10]
What is the difference between an HSA, an Archer MSA, and an MA MSA?
An HSA is funded through contributions made by the policyholder, whereas MSAs are funded by Medicare. Archer MSAs were created to benefit self-employed individuals and employees of certain small employers.[11]
Sources
- IRS 1099-SA Instructions – Death of an Account Holder
- IRS Bulletin, Notice 2004-50 – Distributions
- IRS – Guide to Information Returns
- IRS – Distribution Code Box Instructions
- Form 1099-SA – Instructions for Recipient
- IRS – Recipient TIN Format
- IRS – Account Number Box on Forms
- IRS – Online Fillable Forms
- IRS Form 8889 Instructions – Qualified Medical Expenses
- IRS – Instructions for Forms 1099-SA and 5498-SA
- IRS – Types of Savings Accounts