Updated April 29, 2024
IRS Form W-4, or Employee’s Withholding Certificate, is a form given to an employer by an employee that calculates the amount of federal income tax that should be withheld from the employee’s pay.
A W-4 is not required to be submitted annually unless the employee is exempt from withholding. It is filled out at the start of a job or when an employee wants to update withholdings.
4 Important Facts
Table of Contents |
Previous Versions
Download: PDF
Download: PDF
Download: PDF
When to Use a W4
A W4 is for use by part-time and full-time employees who start a new job or want to change the amount of Federal tax withheld from their paycheck.[3] It is NOT submitted to the IRS and is instead kept on file by the employer.
Not Used
A W4 is NOT used for:
- Independent Contractors: Freelancers and non-corporate businesses should be furnished with a W-9 and then issued a 1099 Form.
- Nonresident Aliens: Instead use a W-8 to provide information to withholding agents to establish foreign status.
Withholding Exemptions
- Exempt employees: Qualified employees EXEMPT from federal withholding use Form W-4 to communicate their exemption status to their employer so that federal taxes are not deducted from their pay.
- Maintaining Exemption: To maintain an exemption, the employee must provide the employer with a new Form W-4 annually indicating their exemption status before February 15th of that year or the next business day if the 15th falls on a weekend.
- Failure to provide: If the employee fails to provide a new W-4, the employer must withhold taxes from wages as if they were single or married filing separately.[4]
Exempt Employee Requirements
To be exempt from federal withholding, employees generally must have no tax liability or a previous exemption claim. Use the Interactive Tax Assistant to find out if wages are exempt from federal income tax withholding.
W4 Form Parts (5)
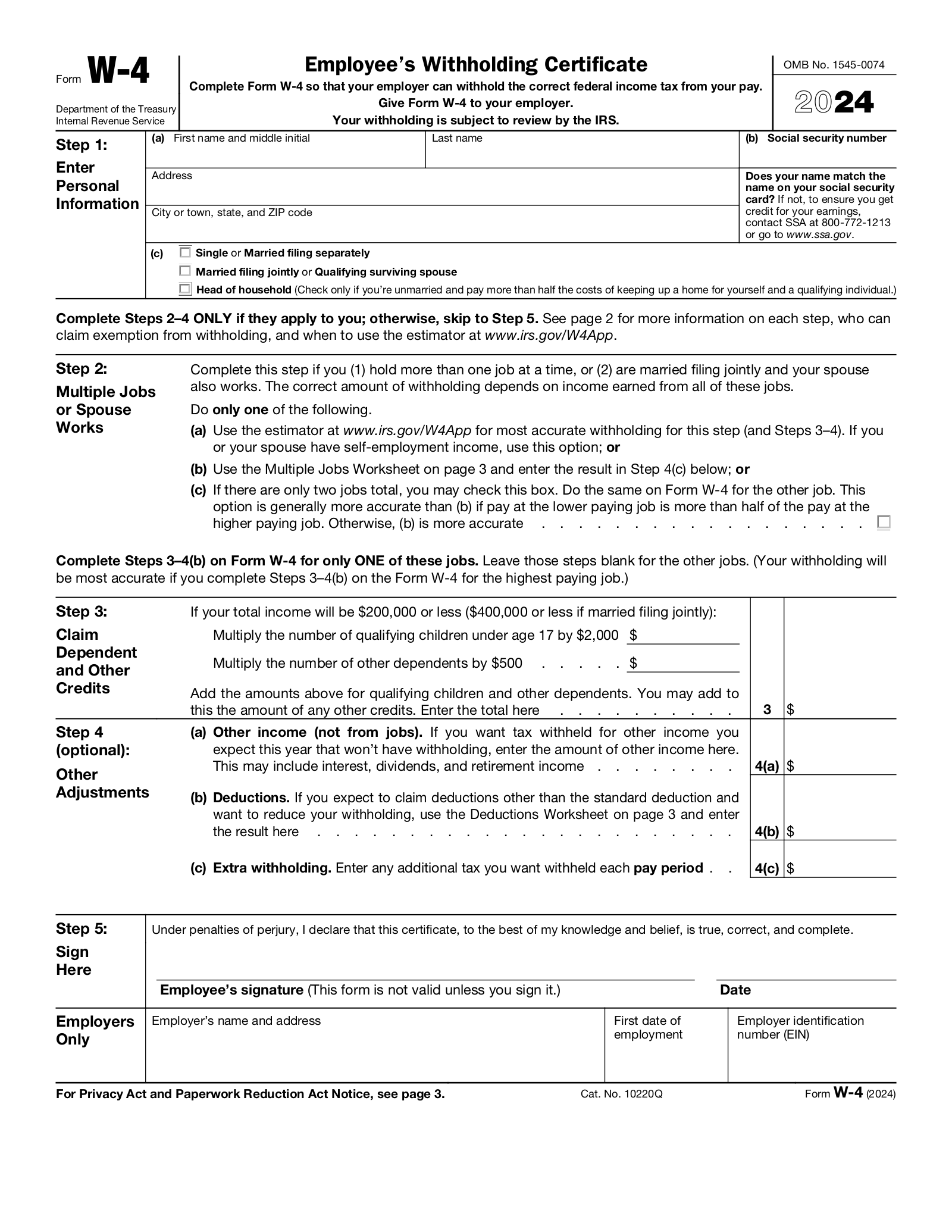
A W4 has five form parts: personal information, an area to list multiple jobs, dependents, additional adjustments, and signatures.
2. Multiple Jobs/Working Spouse

This section is used if you have more than one job or if your spouse also works and your status is married filing jointly.Box 2c should be checked if:
- Your spouse also works, and your status is married filing jointly. It must also be checked on your spouse’s W4; or
- You work two jobs, and the salary of the lower-paying job is greater than half of your primary job.
If you have a second job and the salary of the lower-paying job is less than half of your primary job, complete the multiple jobs worksheet on page 3 of the W4 and record the amount to withhold on line 4(c).
3. Dependents/Other Credits

If you make less than $200,000 or $400,000 when married filing jointly, dependents can be claimed. Lines are available to multiply the number of qualifying children under 17 by $2,000 and other dependents by $500. The total amount is obtained in this section.
*If there are multiple jobs, this section only be completed on one W4 for the most high-paying job. Employees can also use the IRS’s Tax Withholding Estimator to estimate deductions.
4. Other Adjustments

Line 4(a) asks if additional withholding is requested for other types of income that the taxpayer may receive. Some other income types may be:
- self-employment
- retirement
- interest
- dividends
Line 4(b) calculates additional deductions from the deduction worksheet located on page 3.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How long should an employer keep W4s?
The IRS requires that W4s be kept by employers for a minimum of 4 years after the employee signs the document.[5]
Can a W4 be signed electronically?
Yes, a W4 can be sent and signed electronically, but the IRS may request a hard copy for review, which must be printed for submission.
Does a new form have to be filled out every year?
Employees are only required to fill out a W4 once per job.
What if an employee wants to change their withholding amount?
Employees can fill out a new Form W4 and submit it to their employer to change their withholding amount at any time.[6]