Updated February 05, 2024
An IRS form W-9, or “Request for Taxpayer Identification Number and Certification,” is a document used to obtain the legal name and tax identification number (TIN) of an individual or business entity. It is commonly required when making a payment and withholding taxes are not being deducted.
Keep for 4 Years
A W-9 is not filed with the IRS. It is held for documentation purposes and should be kept for 4 years.[1]
How it Works (5 steps)
- Hire. Hire a non-employee to perform services.
- Request W-9. Request a W-9 to be completed by the non-employee.
- Pay. After receiving a completed and signed W-9, payment is made.
- $600 limit. If paid $600 or more per tax year, prepare 1099-NEC.
- IRS Filing. File 1099-NEC with the IRS and send a copy to the non-employee before Jan 31.
Table of Contents |
When is a W-9 Required?
A W-9 must be collected if payment is being made and withholding taxes are not being deducted. Under IRS law,[2] an employer making payments for wages is responsible for collecting withholdings from employees.
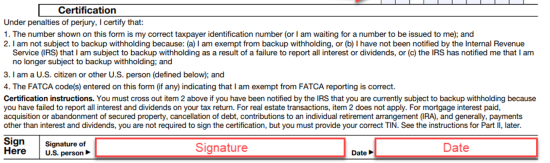
After completion and signing, a W-9 requires a payment recipient to be responsible for the tax liability incurred when accepting a payment.
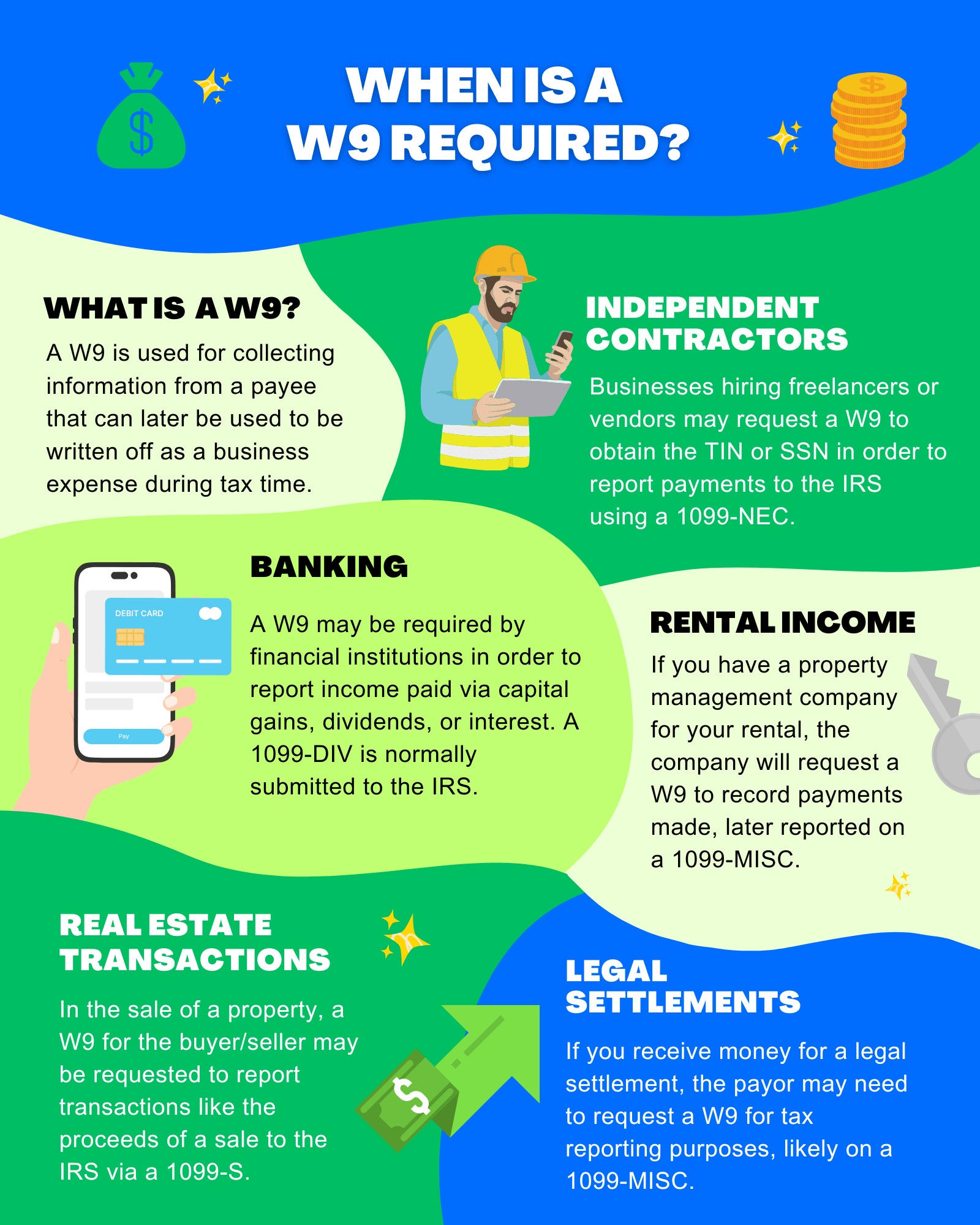
W-9 Common Uses
- Independent Contractors: Businesses hiring freelancers or vendors may request a W-9 to obtain the TIN or SSN to report payments to the IRS using a 1099-NEC.
- Banking: A W-9 may be required by financial institutions to report income paid via capital gains, dividends, or interest. A 1099-DIV is normally submitted to the IRS.
- Rental Income: If you have a property management company for your rental, the company will request a W-9 to record payments made, later reported on a 1099-MISC.
- Real Estate Transactions: In the sale of a property, a W-9 for the buyer/seller may be requested to report transactions like the sale proceeds to the IRS via a 1099-S.
- Legal Settlements: If you receive money for a legal settlement, the payor may need to request a W-9 for tax reporting purposes, likely on a 1099-MISC.
When a W-9 is NOT Required
- Employees: Employee-employer relationships require information about tax withholding that is completed through a Form W-4.
- Personal Payments: Payments to friends or reimbursing someone for personal services do not usually require reporting of payments.[3]
- Tax-Exempt Organizations: Payments made to charities or qualified nonprofits typically do not require a W-9.[4]
- Under IRS Threshold: The IRS reporting threshold is different in some areas. Most commonly, businesses paying for services do not need to collect a W-9 or report income under $600.[5]
How to Fill Out a W-9 (3 parts)
- Download: PDF
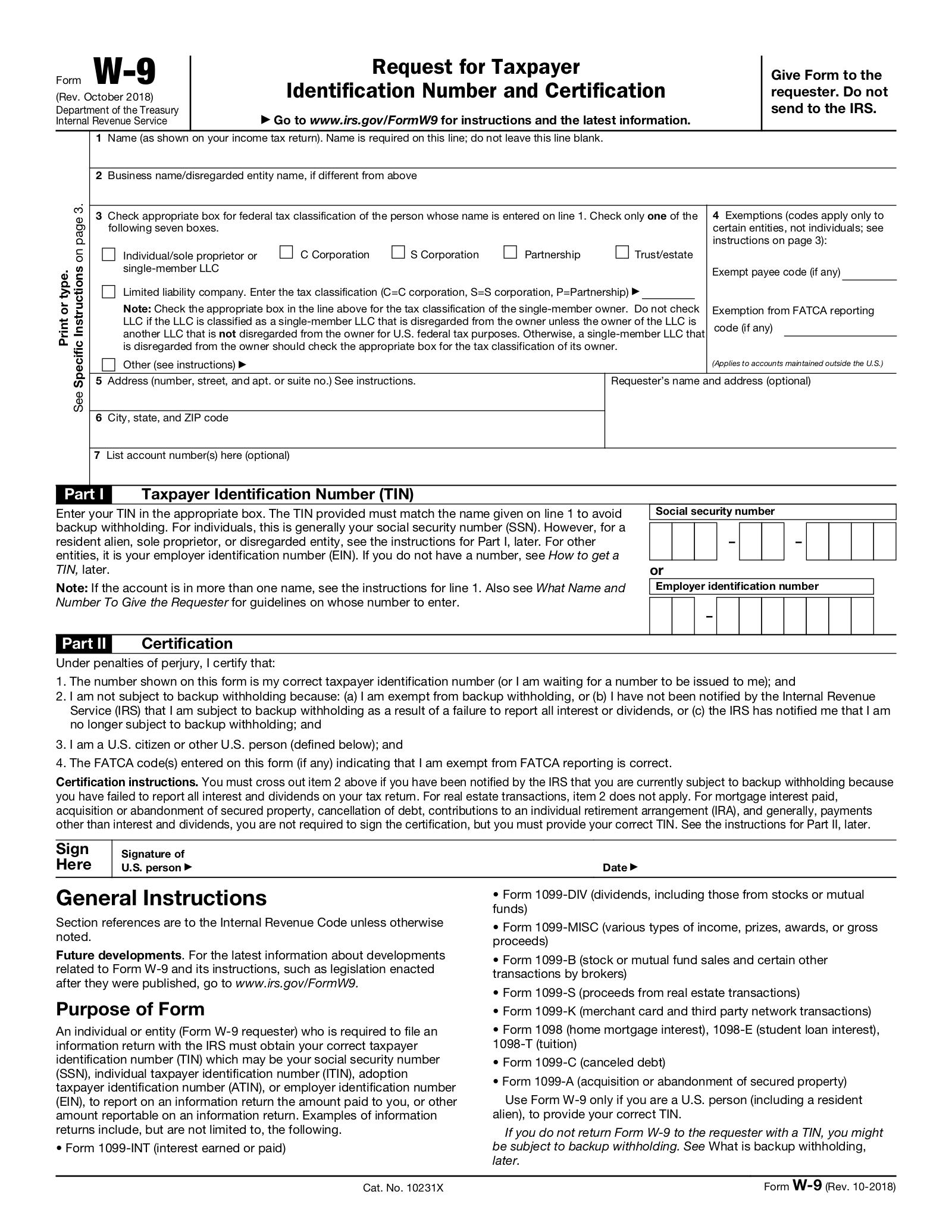
Part 1 – Identifying Information
Line 2. Business name/Disregarded entity name (if different from line 1)
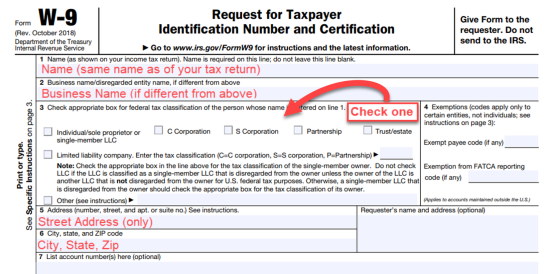
Line 3. Choose tax classification.
-
- Individual/sole proprietor/single-member LLC
- C Corporation
- S Corporation
- Partnership
- Trust/estate
- Limited liability company (LLC) and choose how it is taxed:
- C=C corporation
- S=S corporation
- P=Partnership
- Other
Line 5. Street Address (only)
Line 6. City, State, and Zip Code
Frequently Asked Questions (6)
- What is the penalty for not collecting a W-9?
- Can a W-9 be signed electronically?
- What happens if a contractor refuses to provide a W-9?
- What if a W-9 is incorrect?
- Does the IRS update Form W-9 each year?
- What happens if a W-9 is NOT collected?
1. What is the penalty for not collecting a W-9?
2. Can a W-9 be signed electronically?
3. What happens if a contractor refuses to provide a W-9?
Refusing to provide a W-9 creates compliance issues and must be handled by either:
- Backup Withholding: Invalid TINs or refusal to provide a W9 require the payor to initiate backup withholding, whereby 24% of the contractor’s payment is withheld and paid to the IRS by the payor.[8]
- Termination: The payor may terminate or suspend the vendor’s or independent contractor’s services.
4. What if a W-9 is incorrect?
6. What happens if a W-9 is NOT collected?
What is a W-9? (Video)
Sources
- www.irs.gov/businesses/small-businesses-self-employed/forms-and-associated-taxes-for-independent-contractors
- 26 U.S. Code § 3402(a)(1)
- https://www.taxpayeradvocate.irs.gov/news/tas-tax-tip-use-caution-when-paying-or-receiving-payments-from-friends-or-family-members-using-cash-payment-apps/
- https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/iw9.pdf
- https://www.irs.gov/businesses/small-businesses-self-employed/reporting-payments-to-independent-contractors
- 26 U.S. Code § 6723
- https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-drop/a-98-27.pdf
- https://www.irs.gov/businesses/small-businesses-self-employed/backup-withholding
- https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/p1586.pdf
- https://www.irs.gov/payments/information-return-penalties