Updated June 02, 2022
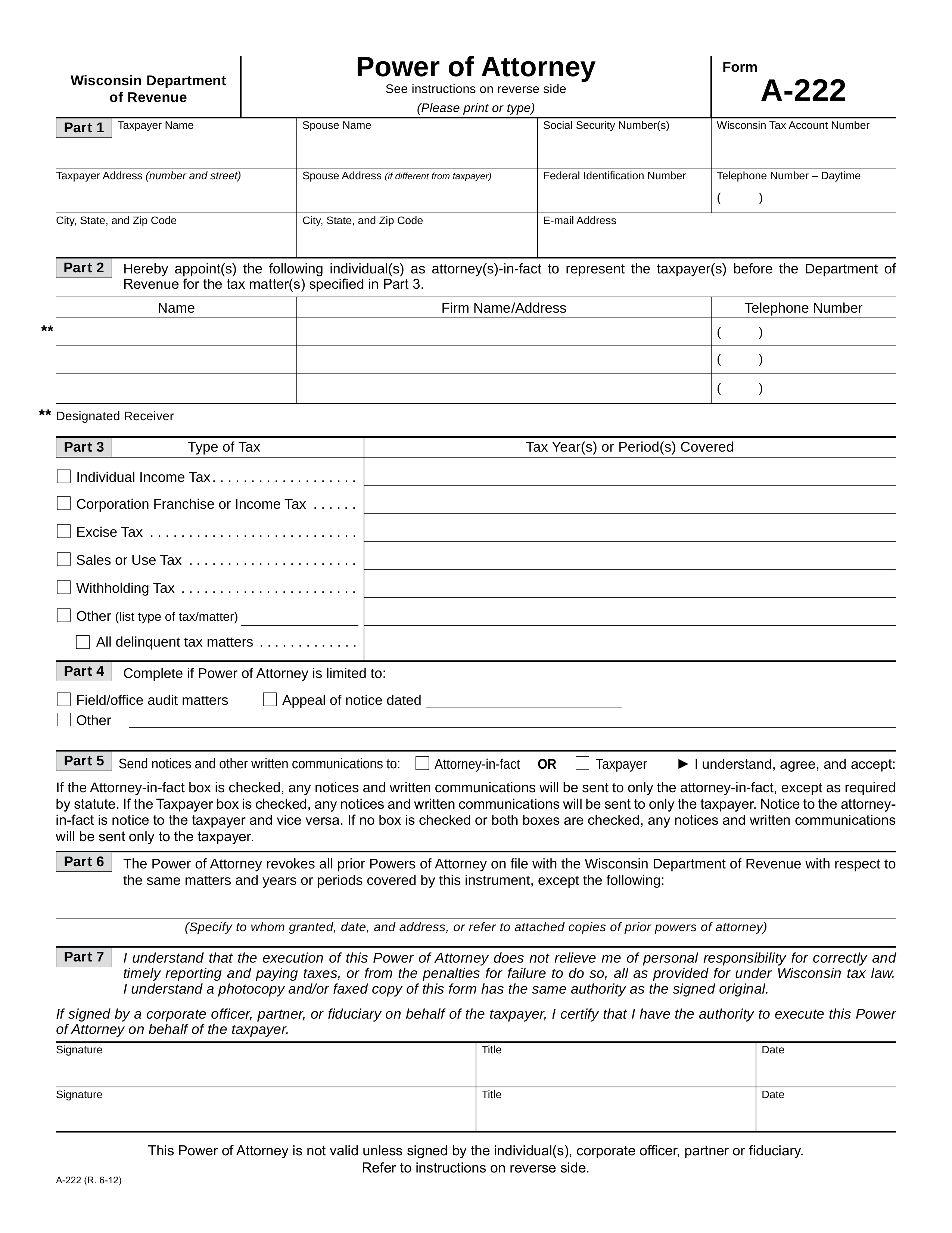
A Wisconsin Tax Power of Attorney (Form A-222) should be employed when you intend to have someone else (i.e. your accountant or tax attorney) handle your paperwork involved with the Wisconsin Department of Revenue on your behalf. Generally, you can name someone to represent your interests and make sure your responsibilities with this entity are satisfied so long as the Wisconsin Department of Revenue approves your choice of agent and the level of power you are granting him or her. This document will enable you to submit the information required for such a decision to be made. Once it has been completed, you (as the principal taxpayer) will need to supply a valid executing signature so that it can be submitted to the Wisconsin Department of Revenue properly.
How to Write
1 – This PDF Wisconsin Tax Form Will Designate An Agent With Principal Powers
The image on this page can be used to view the Tax form using your browser once you click it. You can either save it as a PDF from your browser or you can click on the button below the image labeled “PDF”
2 – The Principal Information Should Be Presented In Part 1
The Principal Taxpayer of this form will have to be fully identified at the start of this document in order for him or her to grant representational Principal Power to an Agent. A table in Part 1 has been made available for this purpose. Use the box labeled “Taxpayer Name” to fill in the First Name, Middle Name, and Last Name of the Principal. The next box in this row (“Spouse Name”) is available for the Full Name of the Principal’s Spouse. This information would be necessary if the Principal filed jointly on any of the matters that he or she will deliver Principal Powers over
The next box in this row (“Spouse Name”) is available for the Full Name of the Principal’s Spouse. This information would be necessary if the Principal filed jointly on any of the matters that he or she will deliver Principal Powers over  The third item of the required information is the Principal’s “Social Security Number.” This should be placed in the third box of this row
The third item of the required information is the Principal’s “Social Security Number.” This should be placed in the third box of this row  The Principal’s “Wisconsin Tax Number” should be supplied to the fourth box
The Principal’s “Wisconsin Tax Number” should be supplied to the fourth box  The first box of the second and third row call for the Principal “Taxpayer Address (Number And Street)” and “City, State, and Zip Code” (respectively)
The first box of the second and third row call for the Principal “Taxpayer Address (Number And Street)” and “City, State, and Zip Code” (respectively)  The next area, consisting of the second boxes in the second and third rows are devoted to the “Spouse Address” and “City, State, And Zip Code.” This information should be recorded if the Principal filed jointly with a Spouse who resides at a different Address then the Principal (i.e. an Ex-Wife or Ex-Husband).
The next area, consisting of the second boxes in the second and third rows are devoted to the “Spouse Address” and “City, State, And Zip Code.” This information should be recorded if the Principal filed jointly with a Spouse who resides at a different Address then the Principal (i.e. an Ex-Wife or Ex-Husband).  In some cases, the Principal Taxpayer may be a Business Entity. If so, then record its Federal Entity Identification Number (FEIN) in the box labeled “Federal Identification Number”
In some cases, the Principal Taxpayer may be a Business Entity. If so, then record its Federal Entity Identification Number (FEIN) in the box labeled “Federal Identification Number”  Use the final two boxes in this table to record the Principal Taxpayer’s “Telephone Number – Daytime” and “E-Mail Address.”
Use the final two boxes in this table to record the Principal Taxpayer’s “Telephone Number – Daytime” and “E-Mail Address.” 
3 – The Attorney-in-Fact Will Be Identified In A Defined Area
The table in “Part 2” will allow three separate Agents or Attorneys-in-Fact to be appointed through this form. The table will have three columns where you may record the Attorney-in-Fact’s “Name,” “Firm Name/Address,” and daytime “Telephone Number.” 
4 – Each Principal Tax Power Being Delivered Must Be Disclosed And Approved
Now, in “Part 3” we will begin the documentation of the Principal Powers that will be delivered by the Principal named in Part 1 to the Agents named in Part 2. A brief table with two columns has been constructed for this purpose. The list of checkboxes in the right column will name the Powers that may be assigned. Only the Principal Powers in this list that have been check marked will be included in the Principal Powers assigned to the Agent. Thus, by marking the appropriate checkbox, the Attorney-in-Fact can have the Principal Authority to represent the Principal with “Individual Income Tax,” “Corporation Franchise Or Income Tax,” “Excise Tax,” “Sales Or Use Tax,” “Withholding Tax,” “Other,” and/or “All Delinquent Tax Matters.” Mark the checkboxes that indicate what areas the Principal wishes to grant Authority to the Agent in. If marking “Other,” you must define the Principal Power the Attorney-in-Fact should have on the blank line after the words “(List Type Of Tax/Matter”).  The column on the right, “Tax Year(s) Or Period(s) Covered” requires that each Tax Matter the Principal will deliver Authority over be accompanied with a definitive time period when the Attorney-in-Fact’s Principal Authority applies. Record the Time Period of a Tax Matter on the corresponding blank line under the second column. If a Tax Matter is unmarked, then it will not be assigned to the Agent’s Principal Power and the corresponding blank line may be left blank (as well).
The column on the right, “Tax Year(s) Or Period(s) Covered” requires that each Tax Matter the Principal will deliver Authority over be accompanied with a definitive time period when the Attorney-in-Fact’s Principal Authority applies. Record the Time Period of a Tax Matter on the corresponding blank line under the second column. If a Tax Matter is unmarked, then it will not be assigned to the Agent’s Principal Power and the corresponding blank line may be left blank (as well).  In some cases, the Principal Taxpayer Authority delivered to the Agent here will only be valid in a certain context. If so, then we will have an opportunity to address these circumstances in “Part 4.” Three checkboxes “Field/Office Audit Matters,” “Appeal Of Notice Dated,” and “Other” have been supplied. If Principal Authority should be limited to either of the first two scenarios, then place a mark in the corresponding checkbox. You may also mark both. If neither of these applies, then you may mark the “Other” checkbox and use the blank line to record the limitation (i.e. “Private Letter Hearing,” “Revocation Hearing,” etc.)
In some cases, the Principal Taxpayer Authority delivered to the Agent here will only be valid in a certain context. If so, then we will have an opportunity to address these circumstances in “Part 4.” Three checkboxes “Field/Office Audit Matters,” “Appeal Of Notice Dated,” and “Other” have been supplied. If Principal Authority should be limited to either of the first two scenarios, then place a mark in the corresponding checkbox. You may also mark both. If neither of these applies, then you may mark the “Other” checkbox and use the blank line to record the limitation (i.e. “Private Letter Hearing,” “Revocation Hearing,” etc.)  In “Part 5,” we will address the subject of Written Notices and other Communications. If the Principal Taxpayer does wish the Attorney-in-Fact to have the Principal Power to be the Recipient of Taxpayer Notices and Communications, then mark the “Attorney-in-Fact” checkbox. If Notices and Communications should be sent to the Principal Taxpayer, then mark the checkbox labeled “Taxpayer.” Note: Only one entity will receive Notices and Communications regarding these Tax Matters
In “Part 5,” we will address the subject of Written Notices and other Communications. If the Principal Taxpayer does wish the Attorney-in-Fact to have the Principal Power to be the Recipient of Taxpayer Notices and Communications, then mark the “Attorney-in-Fact” checkbox. If Notices and Communications should be sent to the Principal Taxpayer, then mark the checkbox labeled “Taxpayer.” Note: Only one entity will receive Notices and Communications regarding these Tax Matters 
5 – Previous Grants Of Authority Should Be Discussed
“Part 6” is only applicable if any Powers of Attorney have been delegated to either the same Tax Matters listed in “Part 3” and/or exists at the same Time Period(s). If so, it should be known this document’s execution will automatically revoke such paperwork. To avoid this, and keep such Power Documents in Effect despite this paperwork’s Execution, list the Attorney-in-Fact’s Full Name and Address from the previous Power Delegation on the blank line in “Part 6” and attach a copy of the previous Power Document that should remain in Effect 
6 – Principal Approval And Execution Is Mandatory For Submission
Part 7 shall supply the space necessary for a proper execution. The Principal must sign this document. If he or she filed jointly with a Spouse, that Spouse will also have to sign this paperwork. If the Principal is a Business Entity, then an Authorized Officer (i.e. President, Vice President, etc.) must sign his or her Name on behalf of the Principal Taxpaying Business Entity. Two rows have been provided in case two individuals must sign this form.
Each Signature Party must sign one of the boxes labeled “Signature.” The box adjacent to this will accept the Principal’s “Title” (in case the Signature Party is signing on behalf of a Business).” The third box in the Signature row will require the “Date” when the Signature Party signed this paperwork to be provided by the Signature Party. This Signature Date must be supplied at the time of Signing.