Updated September 14, 2023
An employee handbook outlines an employer’s rules, benefits, and preferred conduct in day-to-day activities. Every employee should be required to read and sign the handbook after starting employment.
Is a Handbook Required by Law?
An employee handbook is not required under federal law or in any State.
Although, some States require handouts for specific employers.
For example, California requires that organizations of at least five (5) employees must provide an agreement covering sexual harassment, discrimination, and retaliation prevention policies. (Gov Code § 12950.1). All of which are covered in an employee handbook.
Table of Contents |
By Type (7)
Download: PDF, MS Word, OpenDocument
 Medical Office Employee Handbook
Medical Office Employee Handbook
Download: PDF, MS Word, OpenDocument
Download: PDF, MS Word, OpenDocument
Download: PDF, MS Word, OpenDocument
Download: PDF, MS Word, OpenDocument
 Small Business Employee Handbook
Small Business Employee Handbook
Download: PDF, MS Word, OpenDocument
Download: PDF, MS Word, OpenDocument
What to Include (10 steps)
- Mission Statement
- Employment Classes
- Compensation
- Benefits
- Anti-Discrimination
- Immigration Policy
- Non-Disclosure (NDA)
- Dress Code
- Social Media Policy
- Drug Policy
2. Employment Classes
 The classes of employment should be defined including the conditions for termination. Specifically, the following should be described:
The classes of employment should be defined including the conditions for termination. Specifically, the following should be described:
- At-Will Employment – Explains that an employee can be terminated for any reason (with or without cause).
- Eligible Employee – Describes the qualifications for eligible employees which may include part-time off (PTO) and benefits.
- Full-Time Employee – The number (#) of hours required to be qualified as a “full-time” employee.
- Introduction Period – Or “precautionary period, an initial period where an employee is not eligible for benefits.
- Seasonal Employee – For employees hired for a temporary period.
3. Compensation
 All details regarding compensation should be included in this section, including:
All details regarding compensation should be included in this section, including:
- Payment Intervals – It is most common for employees to be paid on a weekly basis.
- Deductions – To mention the types of deductions made to an individual’s paycheck.
- Overtime pay – To inform an employee of the overtime rate. The federal required rate is 1.5x hourly rate for each hour worked beyond 40 hours/week.
4. Benefits
- Employer Benefits – Any type of group benefits sponsored by the employer such as health insurance, 401(k) plans, etc.
- Paid-time off (PTO) – Includes vacation time, sick leave, holidays, and any other days an employee is paid while taking time off.
- Maternity Leave – In accordance with federal law (FMLA), an employee is entitled to twelve (12) weeks off (for both partners).
- Government Benefits – Such as unemployment insurance and social security statements.
- Leaves of Absence – Conditions for when an employee can take unpaid time off.
5. Anti-Discrimination
 There should be clauses mentioned that reflect federal anti-discrimination policies such as:
There should be clauses mentioned that reflect federal anti-discrimination policies such as:
- Equal Opportunity Employer – Discloses that the employer does not discriminate against race, religion, sex, national origin, disability, or veteran status.
- Disability – That the employer agrees to accommodate any person with a disability in accordance with the ADA and ADAAA.
- Sexual Harassment – Lets employees know that harassment of any type is not allowed and how it should be reported.
6. Immigration Policy
 That the employer requires an Employment Eligibility Form (I-9) for each employee. This helps to secure that the individuals being hired are allowed to work in the United States.
That the employer requires an Employment Eligibility Form (I-9) for each employee. This helps to secure that the individuals being hired are allowed to work in the United States.
7. Non-Disclosure (NDA)
 Also known as a “confidentiality agreement”, a non-disclosure agreement (NDA) prohibits an employee from sharing trade secrets to third (3rd) parties.
Also known as a “confidentiality agreement”, a non-disclosure agreement (NDA) prohibits an employee from sharing trade secrets to third (3rd) parties.
9. Social Media Policy
 A social media policy prohibits specific content that can be shared online to social media websites.
A social media policy prohibits specific content that can be shared online to social media websites.
Sample – Employee Handbook
Download: PDF, MS Word, OpenDocument
EMPLOYEE HANDBOOK
OF
[EMPLOYER’S NAME]
Last revised on [DATE]
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- 1 – INTRODUCTION.
- 2 – GENERAL EMPLOYMENT.
- 3 – COMPENSATION.
- 4 – RIGHTS AND POLICIES.
- 5 – STANDARDS OF CONDUCT.
1 – INTRODUCTION
1.1 Welcome
Dear Valued Employee,
Welcome to [ORGANIZATION NAME], a ☐ For-Profit ☐ Non-Profit business entity located in the state of [STATE] (“Employer”). This employee handbook (“Handbook”) contains general information on policies, practices, and benefits of the Employer. It is written to introduce employees to the Employer and get familiarized with it, provide general guidelines on work rules, benefits, and other issues related to employment.
We look forward to working together with you!
1.2 – Purpose of this Handbook
This Handbook, divided into roughly five (5) parts, aims to clarify, explain, and offer a handy reference for the general terms of employment with the Employer, namely general employment details, compensation, benefits, standards of conduct, and the employees’ rights and policies pertaining thereto.
1.3 – Changes in Policy
The Employer reserves the right to modify any policies, benefits, or procedures at any time, excluding the “At-Will Employment” policy in Section 2.1 of this Handbook. Ideally, timely notification will be given to employees, although changes are considered adequate without such notice.
2 – GENERAL EMPLOYMENT
2.1 – “At-Will” Employment
While employed, all employment is considered “at-will,” meaning employees are free to resign at any time and for any reason, with or without notice. Similarly, the Employer is free to conclude an employee’s employment at any time for any lawful basis, with or without cause.
Unlike the general policy changes mentioned in Section 1.3 of this Handbook, which may be amended, modified, or terminated at any time, the policy for at-will employment in this Section is considered immutable except for a situation wherein it is modified via a signed, written agreement between the Employer and the employee at issue.
2.2 – Employment Classifications
For the purposes of salary administration and eligibility for overtime payments and employee benefits, the Employer classifies employees as either exempt (salaried) or non-exempt. Non-exempt employees are entitled to overtime pay in accordance with federal and state overtime provisions. Exempt employees are exempt from federal and state overtime laws and, but for a few narrow exceptions, are generally paid a fixed amount of pay each workweek while they are employed.
- Full-Time. Full-time employees are individuals that work greater or equal to an average of [NUMBER OF HOURS] hours per week. All other employees working fewer hours per week shall be considered part-time.
- Temporary Employees. Some employees may be hired as temporary replacements or to supplement the workforce during a period of higher than usual output. Temporary employee positions are of limited duration and can be let go before the end of the period for which they were originally hired. To confirm, temporary employees are considered “at-will” employees.
- Independent Contractors and Consultants. Independent contractors and consultants are self-employed and not employees as defined by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) under this Handbook.
- Probationary Period. Probation (or probationary period) is a status given to new non-exempt employees for a certain period after being employed by the Employer (“Probation Period”). This status allows the Employer to evaluate the performance of a newly hired employee. The Probation Period will last for a maximum of [NUMBER OF DAYS] days and will conclude with a formal review of the employee by management.
3 – COMPENSATION
3.1 – Payment Schedule
Employees are paid on a ☐ Weekly ☐ Bi-Weekly ☐ Monthly basis. All employees will be paid by check, direct deposit, or by any other means mutually beneficial between the Employer and the employees. In the event a payday falls on a weekend or holiday, employees will be paid the last workday before said payday. If payment is not made before the last workday before said payday, the employees shall be paid as soon as possible afterward.
3.2 – Wages
Exempt employees (as defined in Section 2.2) will be paid based on an annually calculated salary. Non-exempt employees will be paid in accordance with all applicable federal and state laws. All overtime work by non-exempt employees must be approved in advance by the Employer.
3.3 – Deductions and Garnishment
The Employer shall make deductions from an employee’s pay as required by applicable laws, including, but not limited to, deductions for income tax withholding, Social Security and Medicare contributions, and in some cases voluntary deductions for health insurance premiums and other related contributions.
3.4 – Overtime Pay
Overtime is additional compensation that is provided to non-exempt employees when they work more than 40 hours in a workweek and is governed by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). The federal overtime rate is time and one-half per hour worked beyond 40 hours and does not include paid time off (PTO).
3.5 – Paid Time-Off (PTO)
In consideration to provide the best workplace environment, the Employer: (check one)
☐ – Does Not provide paid time off (PTO) as part of employment.
☐ – Provides paid time off (PTO) as part of employment for eligible employees. For non-emergency situations, paid time off (PTO) is required to be requested at least [#] day(s) prior to the requested date and is subject to the Employer’s approval.
Paid time off (PTO) shall include the following types: (check all that apply)
☐ – Bereavement. Eligible employees shall be entitled to [#] day(s) per year to mourn the death of a family member or close friend.
☐ – Jury Duty. If an employee receives a jury summons, the Employer agrees to pay said employee their normal hourly rate during the jury duty for the initial [#] day(s) less any payments received from the court. The employer reserves the right to require any such employee to provide proof of jury duty service and payments made by the court. Employees are expected to return to work if they are excused from jury duty during regular working hours or released from jury duty earlier than expected.
☐ – Personal Days. Eligible employees can take up to [#] personal day(s) per year as paid time off (PTO).
☐ – Sick Days. Eligible employees can take up to [#] sick day(s) per year as paid time off (PTO).
☐ – Vacation Days. Eligible employees can take up to [#] vacation day(s) per year as paid time off (PTO).
☐ – Voting. Eligible employees shall be allowed to take 1 (one) day off per year to vote in any local or federal elections. Said day off shall be considered paid time off (PTO).
☐ – Federal Holidays. Eligible employees shall be entitled to the following days off for the following holidays: (check all that apply)
☐ – Christmas Day
☐ – Columbus Day
☐ – Independence Day
☐ – Juneteenth
☐ – Labor Day
☐ – Martin Luther King Jr Day
☐ – Memorial Day
☐ – New Year’s Day
☐ – Presidents’ Day
☐ – Thanksgiving Day
☐ – Veterans Day
Unused Paid Time Off. If any paid time off (PTO) hours are not used by an employee, the unpaid hours shall be: (check one)
☐ – Forfeited.
☐ – Rolled Over to the next year. The number of hours available to rollover is: (check one)
☐ – Unlimited
☐ – Limited to a maximum of [#] hour(s).
3.6 – Maternity Leave
Eligible employees who are disabled on account of pregnancy, childbirth, or a related medical condition or has a spouse that needs support for such a condition are entitled up to: (check one)
☐ – The minimum time period as required under federal and state law.
☐ – [#] weeks off or the minimum time period as required under federal and state law, whichever is longer.
Such paid time off (PTO) may be requested for prenatal care, severe morning sickness, doctor-ordered bed rest, childbirth, and recovery from childbirth. Eligible employees wishing to take pregnancy leave must give notice to the Employer as soon as possible. Said time periods for maternity leave are calculated on an annual basis and shall be included as paid time off (PTO).
3.7 – Family Medical Leave Act (FMLA)
Eligible employees may request a family and medical leave of absence under the federal Family Medical Leave Act (“FMLA”) for any of the circumstances described below. Employees must request a planned family and medical leave as soon as possible before such leave begins. If the need for the leave is not foreseeable, employees must request the leave as soon as they become aware of the need for leave.
Family and medical leave may be taken for the following reasons:
- To care for an employee’s “serious health condition”;
- To care for an employee’s spouse or registered domestic partner, child, or parent with a “serious health condition”;
- To care for a covered servicemember (the employee’s spouse, child, parent, or next of kin) with a severe illness or injury.
A “serious health condition” is one that requires inpatient care in a hospital or other medical care facility or continuing treatment or supervision by a health care provider.
3.8 – Employer Benefits
The Employer offers the following benefits to eligible employees: (check all that apply)
☐ – Health Insurance. The Employer offers a group health insurance plan to all non-exempt employees. For more information on the specifics of the plan, please consult with the Employer on the specific options and plans.
☐ – 401(k) Plan. The Employer has a 401(k) plan providing a convenient payroll deductible method to help supplement employees’ retirement benefits. For more information on the specifics of the 401(k) plan, employees should consult with the Employer on the specific options and plans.
☐ – Other. [OTHER EMPLOYER BENEFITS]
The Employer offers the aforementioned benefits to eligible employees depending on the type of employment and other factors. This section is not meant to be extensive but rather provides general details about benefits available to employees. Contact the Employer directly for further information about eligibility or the specifics of employee benefits.
3.9 – Government Benefits
In accordance with federal and state laws, every employee shall be entitled to the following government benefits:
- Workers’ Compensation. Any employee who is unable to work due to a work-related injury or illness shall be eligible for Workers’ Compensation benefits in accordance with federal and state laws.
- Social Security Benefits (FICA). Both the Employer and the employees contribute funds to the federal Social Security program. This program is intended to provide the employees with retirement benefit payments and medical coverage upon reaching retirement age.
- Unemployment Insurance. The Employer pays federal and state taxes on all paychecks to provide employees with unemployment insurance coverage in the event they become unemployed through no fault of their own and due to other circumstances described by law. State agencies directly administer this insurance and determine benefit eligibility, amount (if any), and duration.
4 – RIGHTS AND POLICIES
4.1 – Equal Opportunity Employment
The Employer is an Equal Opportunity Employer, meaning employment opportunities are based upon one’s qualifications and capabilities to perform the essential functions of a particular job and free from discrimination because of race, religion, sex, national origin, age, veteran status, disability, genetic information, or any other characteristic protected by law.
The Employer’s Equal Employment Opportunity policy governs all aspects of employment including, but not limited to, selection, job assignment, compensation, discipline, termination, and access to benefits and training.
4.2 – Immigration Law Compliance
The Employer is committed to employing only United States citizens and aliens authorized to work in this country. In compliance with the Immigration Reform and Control Act of 1986, as amended, each new employee, as a condition of employment, must complete the Employment Eligibility Verification Form I-9 and present such documentation establishing the identity and eligibility of an employee. Former employees who are rehired must also meet the same said documentation if they have not in the past three (3) years.
4.3 – Accommodation for Employees with Disabilities
The Employer agrees to comply with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), as amended by the ADA Amendments Act (ADAAA), and all applicable federal, state, and local fair employment practice laws and is committed to providing equal employment opportunities to qualified individuals with disabilities.
If any employee believes they need an accommodation due to a disability, said employee is responsible for requesting any such accommodation from the Employer.
An employee may make such requests orally or in writing and to include relevant information, such as:
- A detailed description of the accommodation being requested;
- A detailed reason for the accommodation; and
- How the accommodation will help said employee perform the essential functions of their duties and responsibilities.
4.4 – Minors
The Employer will hire in accordance with the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) regulations pertaining to the employment of minors, in addition to any state regulations, including, but not limited to, hiring minors above the age of 14 years, assigning limited hours to employees under the age of 16 years, and only hiring employees above the age of 18 years for any work that might be deemed as hazardous.
4.5 – Relatives of Employees
In pursuit of best practices, the Employer reserves the right to decline employing an individual who is a relative of an employee or reassign or terminate the employment of someone who becomes the relative of another employee during the course of their employment. In the latter case, the employee must disclose, as soon as possible, if an employee is of another employee’s relation to the Employer.
4.6 – Privacy
The Employer is respectful of each employee’s privacy. All employee information, including but not limited to personal, demographic, and any other personal details, will be shared as required in day-to-day business activities.
4.7 – Confidentiality
The Employer takes its protection of trade secrets and confidential business information in a strict manner. All employees must maintain trade secrets and other confidential business information in confidence. Although, employees are free to discuss such issues with co-workers or third (3rd) parties for the purpose of improving work conditions. Employees found to violate this policy will be subject to disciplinary action, up to and including termination of employment.
5 – STANDARDS OF CONDUCT
5.1 – General
The Employer’s rules and standards of conduct are essential to a productive working environment. All employees must familiarize themselves with the Employer’s rules, and standards as each employee will be held to them.Theft or inappropriate removal or possession of the Employer’s property;
- Falsification of an employee’s timekeeping records;
- The possession, distribution, sale, transfer, public discussion, or use of alcohol or illicit drugs in the workplace;
- Fighting or threatening violence in the workplace;
- Gossiping or spreading rumors about other employees;
- Boisterous or disruptive activity in the workplace;
- Negligence or improper conduct leading to damage of Employer-owned or customer-owned property;
If an employee should have further questions regarding the aforementioned standards of conduct, they should speak directly with the Employer.
5.2 – Attendance
Absenteeism and tardiness place an undue burden on other employees and on the Employer as a whole. The Employer expects that every employee will be regular and punctual in their attendance. Employees are also expected to return from scheduled breaks and meal periods on time.
5.3 – Dress Code
The Employer and its employees agree that there is: (check one)
☐ – No Dress Code required as part of the day-to-day workplace conditions.
☐ – A Dress Code required as part of the day-to-day workplace conditions and is described as: [DRESS CODE REQUIREMENTS]
If the dress code is not followed, immediate disciplinary actions may be taken, which may include termination of employment.
5.4 – Safety
The Employer is committed to providing a clean, safe, and healthful work environment for its employees. Maintaining a safe work environment, however, requires the continuous cooperation of all employees. All employees must comply with all occupational safety standards and health regulations established by the Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA) including state and local laws.
5.5 – Discrimination and Sexual Harassment
Sexual harassment is a form of discrimination and is prohibited by law. For the purposes of this policy, sexual harassment is defined as unwelcome sexual advances, requests for sexual favors, and other verbal or physical conduct of a sexual nature when this conduct explicitly or implicitly affects an individual’s employment, unreasonably interferes with an individual’s work performance, or creates an intimidating, hostile, and offensive work environment.
5.6 – Substance Abuse
The Employer is committed to maintaining a workplace free of substance abuse. No employee shall be allowed to consume, possess, sell, purchase, or be under the influence of alcohol or illegal drugs at the workplace or during work hours. The use of over-the-counter medications and legally prescribed drugs is permitted as long as they are used in the manner for which they were prescribed and provided that such use does not hinder an employee’s ability to perform their job safely.
As part of the Employer’s guidelines: (check one)
☐ – No drug testing is required as part of any person’s employment with the Employer.
☐ – Drug testing is required as part of a person’s employment with the Employer. All drug tests shall be administered in accordance with federal, state, and local laws and may be unannounced prior to administering a drug test.
5.7 – Social Media Policy
It is extremely important that all employees use common sense and careful judgment when communicating with others online. The Employer strives to maintain a workplace free of harassment and sensitive to the diversity of its employees. Therefore, the Employer prohibits the use of electronic devices and other communication systems that are disruptive, offensive to others, and directly or indirectly harmful.
5.8 – Disciplinary Action
The Employer’s disciplinary action is intended to fairly and impartially correct behavior and performance problems early on to prevent reoccurrences. Disciplinary action may involve a verbal warning, written warning, suspension, or termination of employment, depending on the severity of the problem and the frequency of occurrence. The Employer reserves the right, at their sole discretion, to change, suspend, or cancel, with or without notice, all or any part of the policies, procedures, programs, and benefits discussed in this Handbook.
This Handbook is effective as of the undersigned date and may be updated at any time.
I, as an employee, acknowledge that I have read and agree to the above terms and conditions made in this Handbook.
Employee Signature: ______________________ Date: ___________
Print Name: _____________________________
How to Write
Download: PDF, MS Word, OpenDocument
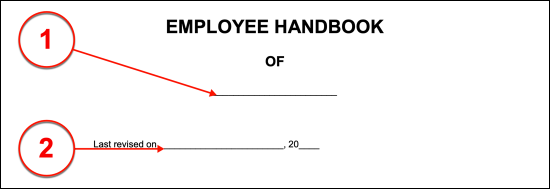
I. Handbook Title Page And Introduction
(1) Issuing Entity Name. The title page of this handbook requires some information so that it may be easily recognized. Produce the name of the Company that is issuing this handbook on the blank line in the title.
(2) Version. The most recent revision date of this handbook will inform the reader (and the å) whether it is the most up-to-date handbook available to Employees from the Issuing Company. Furnish the date of the last time this handbook was edited, revised, or changed in any way.
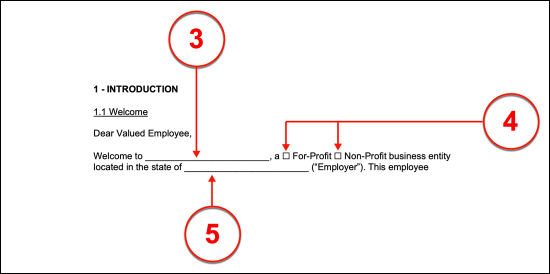
(3) Company Name. The full name of the Company should be confirmed in the introduction displayed in Section I. Produce the full legal name of the Issuing Company to the first space on display in the introduction.
(4) Type Of Hiring Company. A basic choice will need to be made as a part of the introduction. The type of Company that is issuing this handbook will need to be properly categorized. This can be accomplished by either placing a mark in the “For-Profit” checkbox to categorize the Issuing Company as one that operates to make a profit or by marking the “Non-Profit” checkbox to establish the Issuing Company as one that does not operate to make money or a profit. Only one of these checkboxes may be selected
(5) State Of Jurisdiction. The State where the Issuing Company (the Employer) was legally established and whose laws apply to its behavior must be documented during the introduction as well. Seek out the second empty line in the introduction then produce the entire legal name of the Employer or Issuing Company.
II. General Employment Conditions
(6) For Full Time Employee. The next area that requires attention is found in Section “2.2 Employment Classifications.” Here, any Employee receiving this handbook must be informed of the number of hours a week that he or she must work to be considered a Full-Time Employee of the Company. To this end, document the exact number of hours that must be worked every week to qualify as a Full-Time Employee in the space provided in Statement (A).

(7) Probationary Requirement. The second section will also serve to inform the Employee of the length of time that constitutes the amount of time that the new hires will be on probation. Since this may differ from Employee to Employee, the longest probation period this Employer expects of new hires should be documented in Statement (D).

III. Compensation
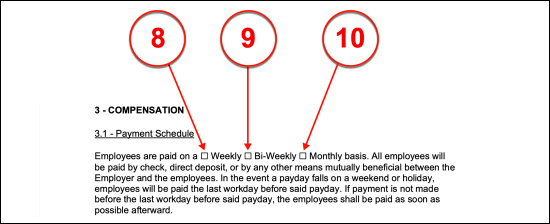
Select Item 8, Item 9, or Item 10
(8) Weekly Payment. Section 3.1 will also request that some information be documented for the benefit of the Employee’s edification. The first topic of discussion in this section will be the compensation the Employer shall pay the Employee. The frequency of these payments must be presented in this section by selecting one of three checkboxes. If the Employee will be paid once a week, then the “Weekly” box must be selected
(9) Bi-Weekly Payment. If the Employee is paid once every two weeks the “Bi-Weekly” checkbox should be selected.
(10) Monthly Payment. If neither of these applies and the Employee will be paid once a month then choose the “Monthly Basis” checkbox.
Select Item 11 Or Select Item 12
(11) No PTO. Whether the Employer will pay the Employee for time off in certain conditions or not must be established in this handbook. Section 3.5 will allow the quick production of definitive information the Employee will need with a presentation of two basic checkbox statements. If the Employer does not pay for any time off under any circumstances, then select the “Does Not” checkbox statement. If the Employer does not grant paid time off then, proceed to Item 20.

(12) PTO Provided. If the Employer does grant paid time off, then select the second checkbox statement in Section 3.5. Some additional discussion will be necessary for this selection beginning with a record of the number of days that the Employee must give as notice during when requesting paid time off. Once done, review Items 11 through 19 so that all applicable PTO’s (paid time off) can be established and reported to the Employee reviewing this literature.

Discuss Items 13 Through 19 As Needed
(13) Bereavement. If the Employer shall provide payment during the Employee’s requested time-off should it be to mourn a Family Member or Loved One then select the “Bereavement Statement.” The number of days the Employee will be allowed to take off while being paid for “Bereavement” must also be established by recording it in the space available.

(14) Jury Duty. When an Employee is called to act as a Juror he or she can still be eligible for paid time off provided this is established in the handbook. Select the second checkbox statement if the Employer will pay the Employee for some or all of his or her time off needed for jury duty. This statement allows for a specific number of days to be named when the Employee will be eligible for full pay (minus the amount paid by the State or Federal Government for serving as a jury). Supply the number of days when the Employee will be paid his or her pay rate to this statement in the space provided. It should be noted this number of days of paid time off shall apply beginning on the first date when jury duty begins.

(15) Personal Days. Some Employers will grant a number of days off from work to the Employee for personal reasons. Select the “Personal Days” checkbox if this will be the case. Additionally, provide the number of personal days that will be allotted to the Employee every one year when he or she may take time off from work for personal reasons and still be paid by the Employer in the space provided.

(16) Sick Days. If the Employer intends to pay the Employee for days he or she does not work because of sickness then the fourth checkox statement must be selected. Additionally, the maximum number of sick days off that the Employer will pay the Employee should be indicated with an entry to the space this statement provides.

(17) Vacation Days. Some Employees will be eligible for a number of paid vacation days. The fifth statement in this list should be selected and the maximum number of days that may be taken by the Employee as a paid vacation must be defined in the space provided.

(18) Voting. If the Employer will pay the Employee for one day per year to vote in a local election or federal election, then the “Voting” checkbox must be chosen.

(19) Federal Holidays. If the Employer will continue to pay the Employee during time off for a “Federal Holiday” then mark the seventh checkbox must be selected. In addition to selecting this statement, each federal holiday that the Employer will give the Employee as paid time off must be selected from the list provided. Bear in mind, that any holiday selected from this list will be considered a holiday that the Employee will not be obligated to work during and still be entitled to his or her normal pay rate.

Select Item 20 Or Complete Item 21
(20) Forfeited Time Off. Oftentimes, the Employee will not take the maximum amount of paid time off allowed to him or her during the year. If he or she will not be allowed to add it to the next year’s allowed paid time off, then select Statement (A) from Section 3.5.
(21) Rolled Over Time Off. If the Employee will be allowed to take apply any paid time off to the next year then choose the checkbox labeled “Rolled Over.” An additional choice will need to be made. If the Employee may roll over the maximum amount of paid time off that he or she has not taken during one year to the next year, then the “Unlimited” checkbox should be selected. However, if a limit will be imposed then choose the “Limited…” statement and produce the maximum number of hours of unused paid time off for one year that may be applied to the next year in the space provided.

Choose Item 22 Or Choose Item 23
(22) Minimum Maternity Leave Available. The Employer will be obligated to meet the minimum amount of time off given to the Employee as a result of the Employee being unable to work due to pregnancy/childbirth and similar medical conditions or that Employee’s Spouse is disabled because She is disabled by pregnancy/childbirth and related medical issues.
(23) Number Of Weeks Off Maternity Leave. If the Employer opts to allow time off for the Employee (or his or her Spouse’s) pregnancy, childbirth event, and other related medical conditions then the second checkbox statement should be selected and the maximum amount of paid time off allowed should be documented in the space provided.

Select From Items 24 Through Item 29 As Needed
(24) Health Insurance. Section 3.8 Employer Benefits will allow the Employer to document which benefits the Employee may (potentially) participate in during his or her employment. Select “Health Insurance” if the Employee will be allowed to participate in a group health insurance plan provided by the Employer.

(25) Life Insurance. The second checkbox must be selected if the Employer will offer the Employee a life insurance plan through its current available programs.

(26) Flexible Spending Account. If the Employer has set up an account or program where the Employee may have some of her pay withheld and saved for out of pocket medical expenses (both for the Employee’s health or his or her Dependent’s health), insurance premiums, and other related Health Care functions then select the “Flexible Spending Account (FSA)” statement. Naturally, such withholding will be done before taxes are subtracted from the Employee’s payment.

(27) 401(k) Plan. Select the next checkbox statement if the Employer has set up a 401(k) plan to aid the Employee’s efforts to prepare for retirement.

(28) Commuter Benefits. Some Employers will have set up programs to aid the Employee in getting to and from work through public transportation. Such a program involves withholding a certain amount from the Employee’s payment before taxes are applied then funnels this money into a commuter program that the Employer makes available to the Employee at the request of the Employee. Select the fifth list item if the Employer issuing this handbook has set up such a program.

(29) Other Benefits. If the Employer participates in other programs that can provide benefits to the Employee that remains undefined by this list then place a mark in the “Other Benefits” checkbox and use the space provided to define every benefits package available to the Employee left uncovered by this list.

V. Standards Of Conduct
Select Item 28 Or Select Item 29
(30) No Dress Code. A few more issues will need to be handled before this handbook may be considered ready for the Employee’s acknowledgment. Section 5.3 will inform the Employee of any dress code policy that may be required by the Employer. This policy must be defined even if “No Dress Code” requirement will be imposed by the Employer. Therefore, if the Employer has not imposed a dress code where Employees will be expected to dress a certain way or refrain from predetermined items/fashion then select the “no Dress Code” statement.
(31) Dress Code Requirement. If the Employer expects Employees to wear a uniform, dress according to a defined standard, or refrain from dress items, accessories or other fashions then select the second statement (labeled “Dress Code.”) After making this selection, the manner or way the Employees must dress when working will require must be defined in the space this statement provides.

Select Item 32 Or Select Item 33
(32) No Drug Testing. If the Employer has not instituted a substance abuse or drug policy that requires the Employee to submit to drug testing, then select the “No Drug Testing” checkbox.
(33) Drug Testing Requirement. If the Employee will be obligated to submit to “Drug Testing” (so long as such tests are conducted in compliance with local and federal law) then select the second checkbox statement in Section 5.6

VI. Employee Signing
(34) Employee Signature Acknowledgment. After he or she has read the handbook, the Employee must sign then print his or her name as an acknowledgment of receiving and understanding its content.
(35) Employee Signature Date. The date when the Employee signs his or her name to officially acknowledge the content of this handbook must be submitted as he or she provides the required signature.









 A welcome message should be included with a brief description of the organization’s purpose. This is often referred to as a ‘mission statement’ that gives an employee a quick summary of the organizational culture.
A welcome message should be included with a brief description of the organization’s purpose. This is often referred to as a ‘mission statement’ that gives an employee a quick summary of the organizational culture. To include if there is any dress ware that is required such as a uniform or other professional attire.
To include if there is any dress ware that is required such as a uniform or other professional attire. Whether alcohol or drugs are accepted at the workplace and if the employer conducts drug testing.
Whether alcohol or drugs are accepted at the workplace and if the employer conducts drug testing.